Limitation
-
The scope of the proposed workflow is broad and, therefore, complete coverage is challenging.
-
It is very unrealistic to consider that human analyst can be removed from the process of annotation.

The proposed methodology is designed for the human analyst (mostly researchers in Linguistics).
Therefore, we assume that the methodology is general enough to be useful for broad class of research applications.
Different analytical domains - e.g. speech and gesture - and theoretical perspective require a rigorous organization of the annotation procedure.
The scope of the proposed workflow is broad and, therefore, complete coverage is challenging.
It is very unrealistic to consider that human analyst can be removed from the process of annotation.

A very large number of dimensions have been annotated in the past on mono and multimodal corpora. To quote only a few, some frequent speech or language based annotations are speech transcript, segmentation into words, utterances, turns, or topical episodes, labeling of dialogue acts, and summaries; among video-based ones are gesture, posture, facial expression [...].
(Popescu-Belis, 2010)
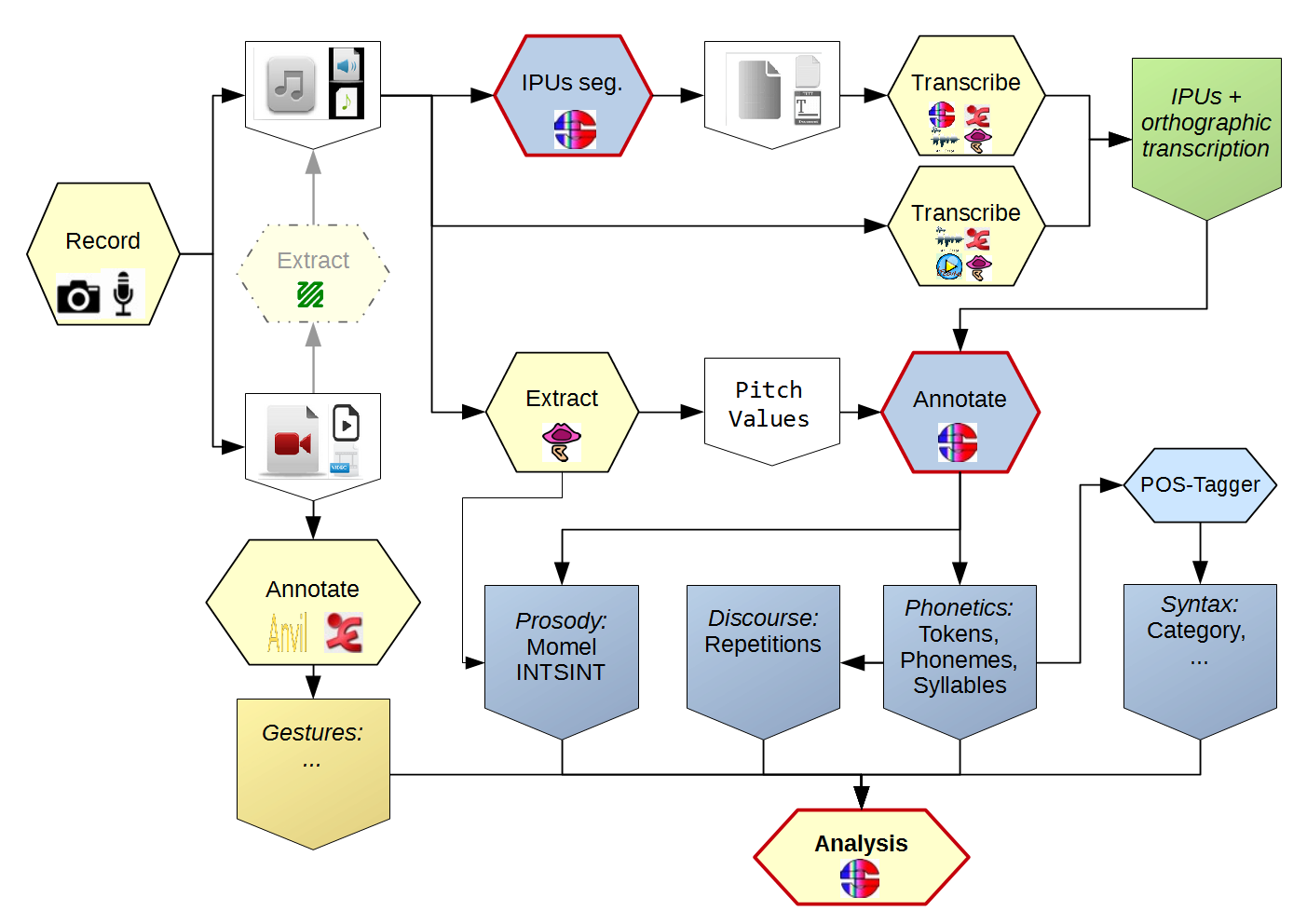
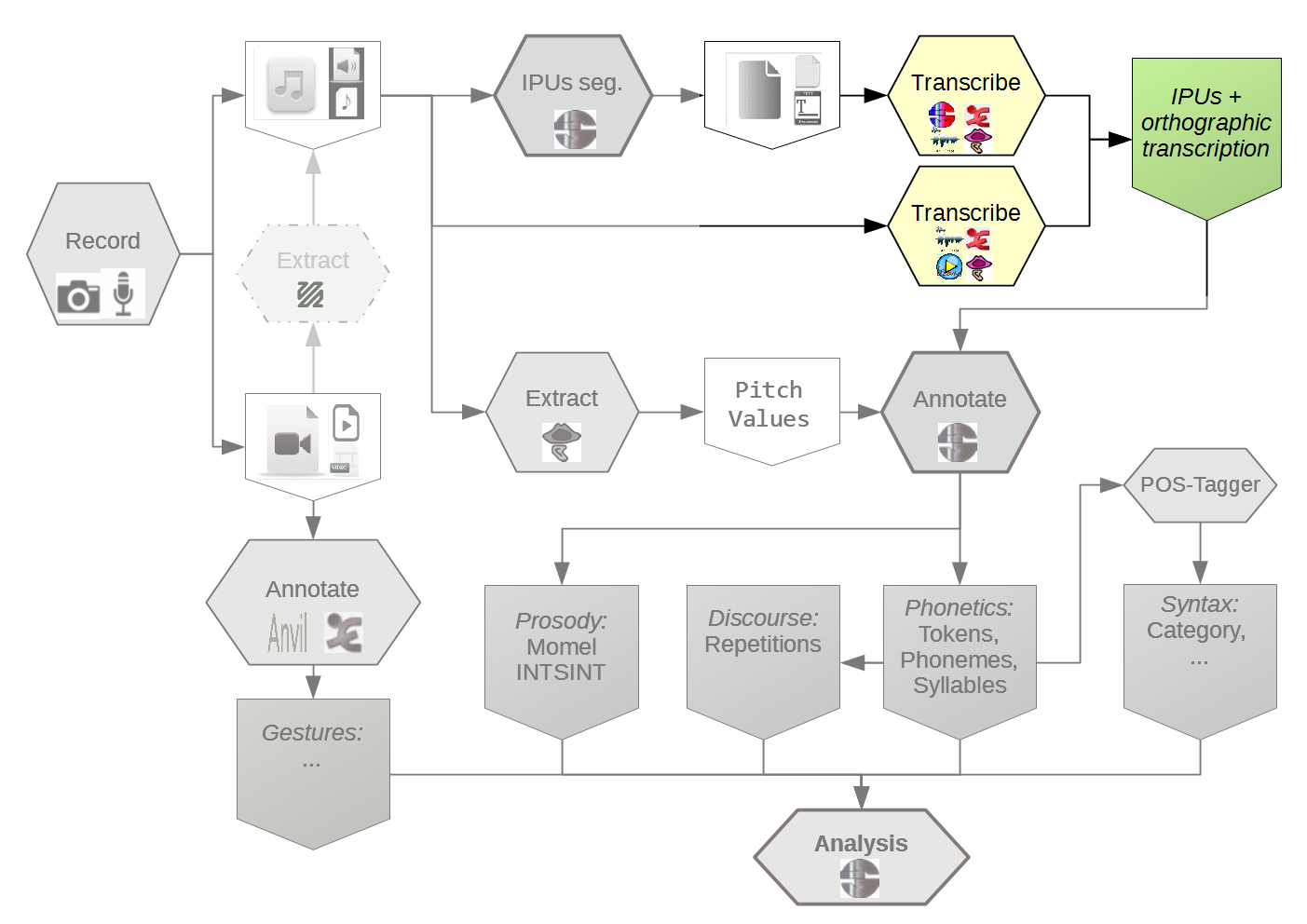
In this tutorial, we will report on:
Garbage in, Garbage out.
The capture of multimodal corpora requires complex settings such as instrumented lecture and meetings rooms, containing capture devices for each of the modalities that are intended to be recorded, but also, most challengingly, requiring hardware and software for digitizing and synchronizing the acquired signals.
(Popescu-Belis, 2010)



The number of devices is also important.
Lack of standardization means that fewer researchers will be able to work with those signals.
Of course, provide 44100Hz

A short list of software we already tested and checked:





An EOT must include, at least:

donc + i- i(l) prend la è- recette et tout bon i(l) vé- i(l) dit bon [okay, k]
ah mais justement c'était pour vous vendre bla bla bla bl(a) le mec i(l) te l'a emboucané + en plus i(l) lu(i) a [acheté,acheuté] le truc et le mec il est parti j(e) dis putain le mec i(l) voulait
euh les apiculteurs + et notamment b- on n(e) sait pas très bien + quelle est la cause de mortalité des abeilles m(ais) enfin il y a quand même + euh peut-êt(r)e des attaques systémiques
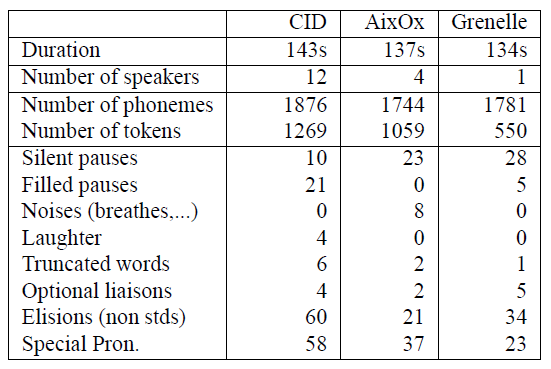
The automatic systems must be adapted to deal with EOT
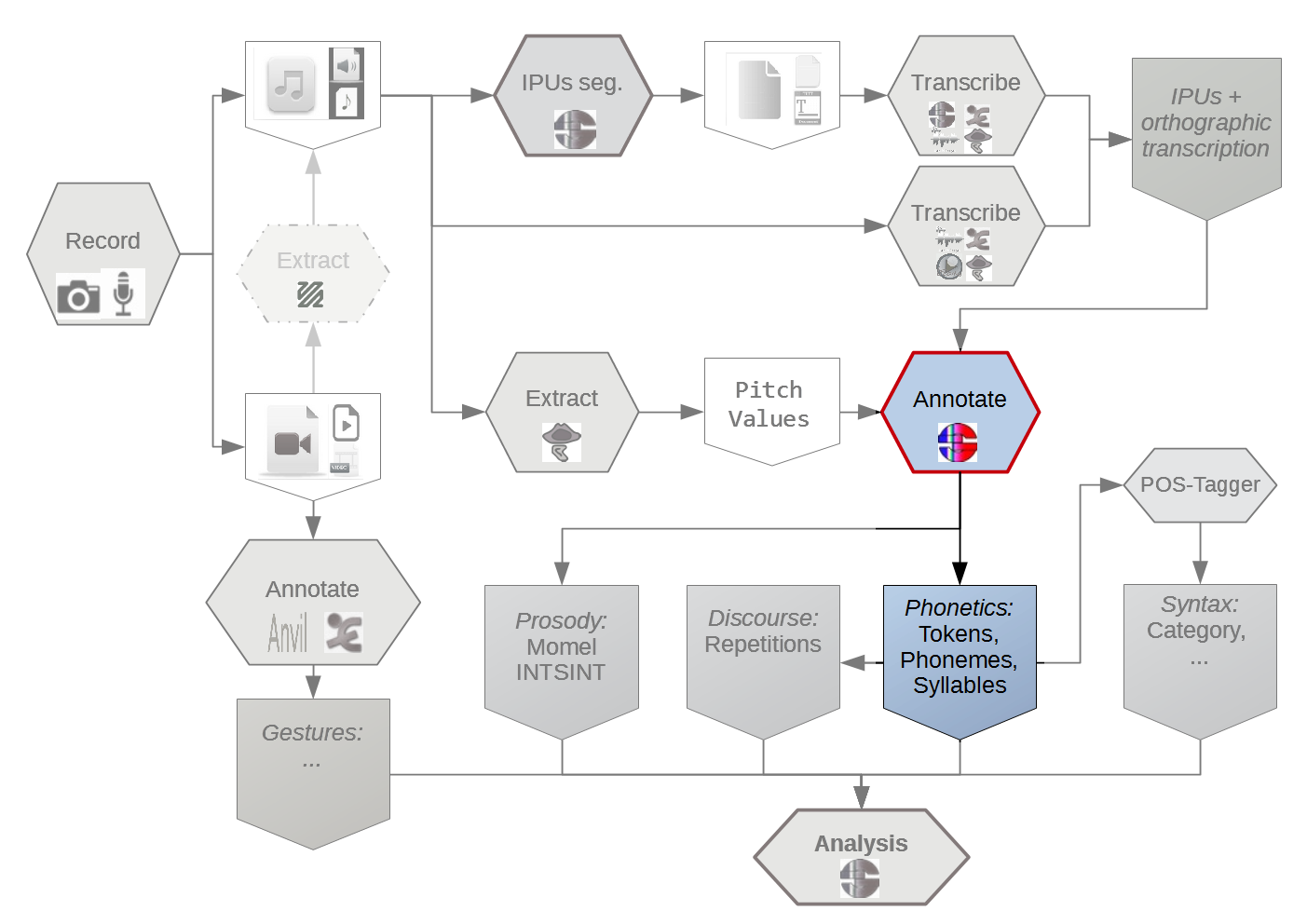
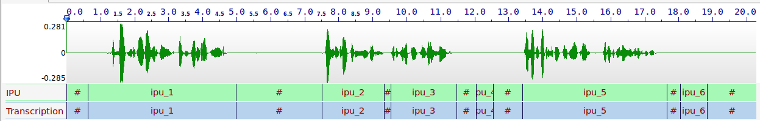
The main steps of the text normalization proposed in SPPAS are:
This is + hum... an enrich(ed) transcription {loud} number 1!
(Bigi 2011)
Converting from written text into actual sounds, for any language, cause several problems that have their origins in the relative lack of correspondence between the spelling of the lexical items and their sound contents.
(Bigi 2013)
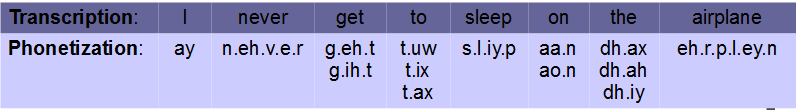
By convention, spaces separate words, dots separate phones and pipes separate phonetic variants of a word. For example, the transcription utterance:

In (Bigi et al. 2012), we compared 3 types of OT:
Evaluations compare a reference phonetized manually to phonetizations obtained with SPPAS

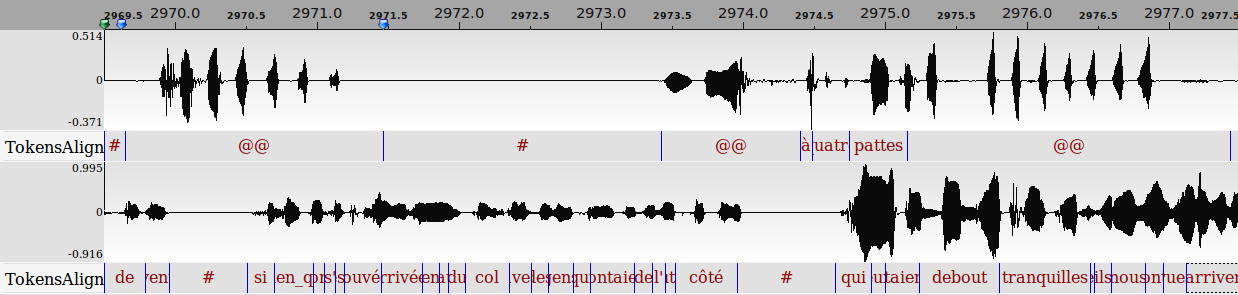
Manual alignment has been reported to take between 11 and 30 seconds per phoneme.
(Leung and Zue, 1984)



SPPAS (python+Julius), available for English, French, Italian, Spanish, Catalan, Polish, Japanese, Mandarin Chinese, Taiwanese, Cantonese
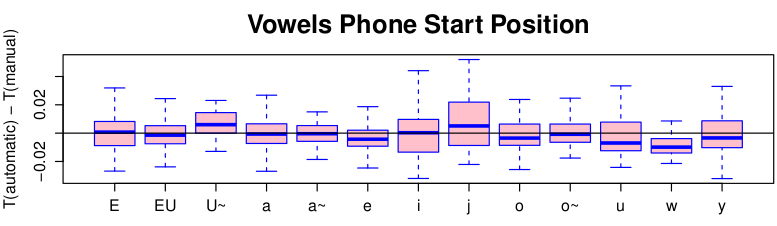

(Bigi et al. 2010)

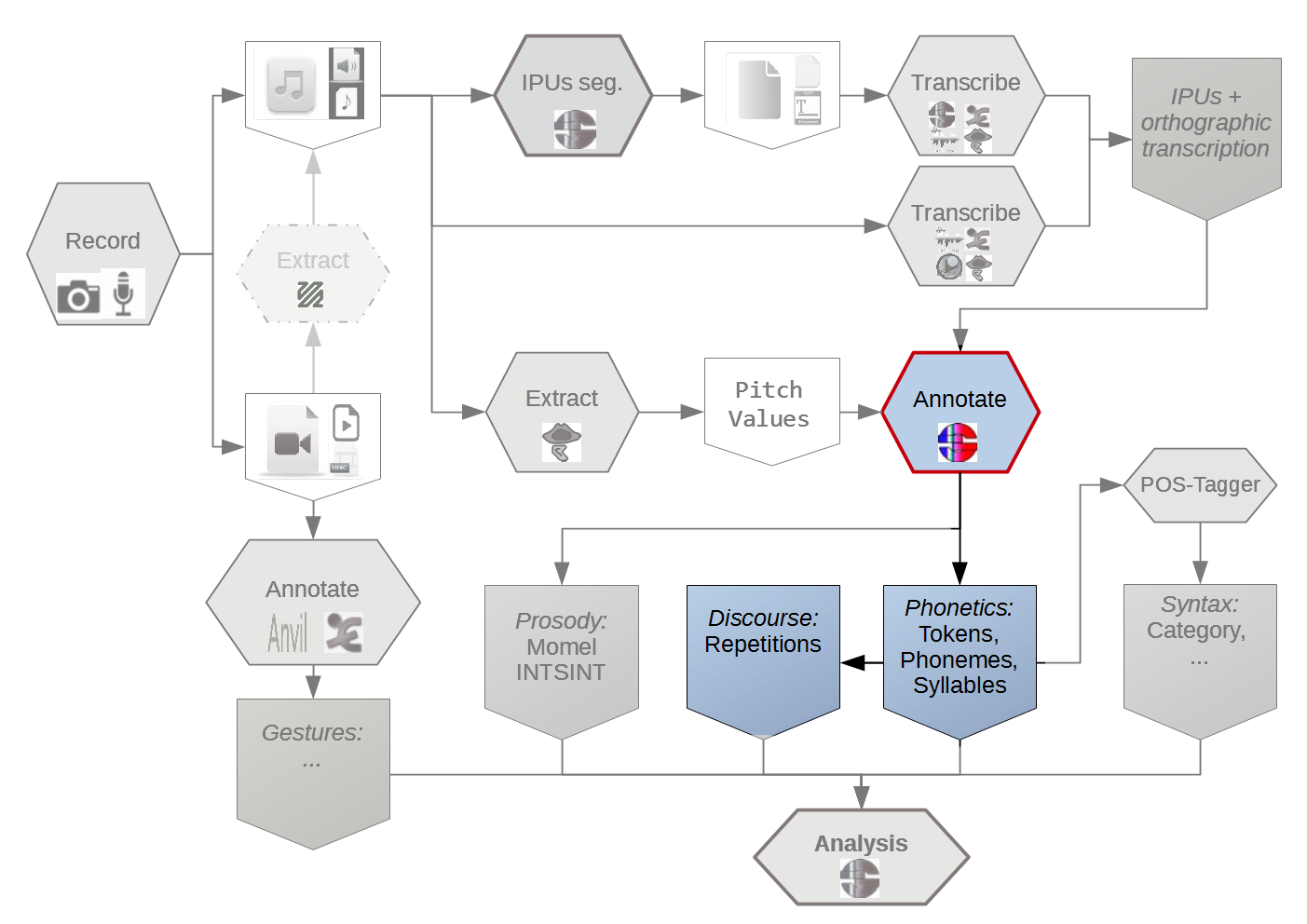
(Bigi et al. 2014)
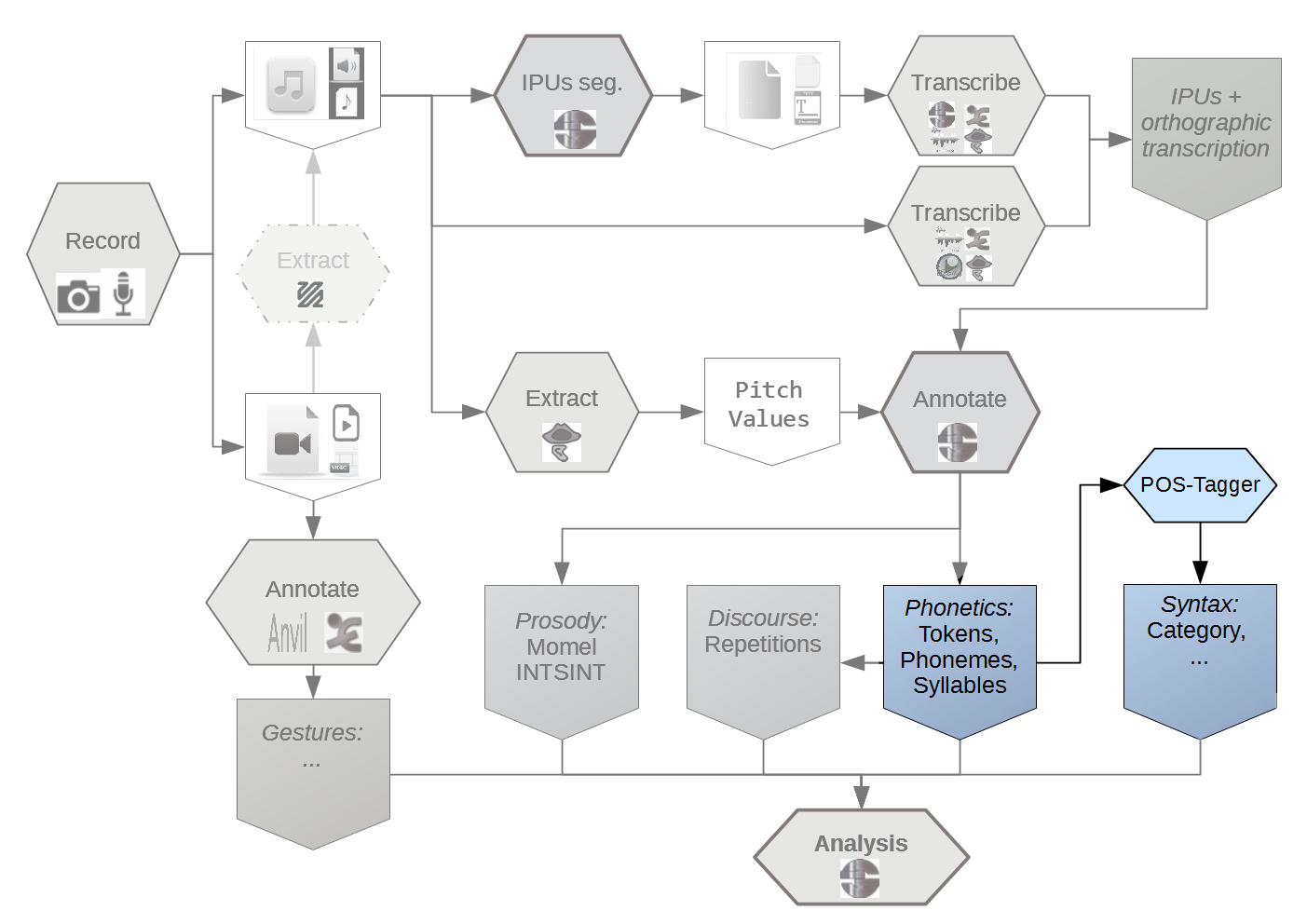
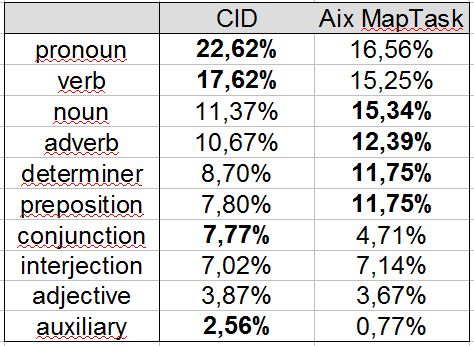
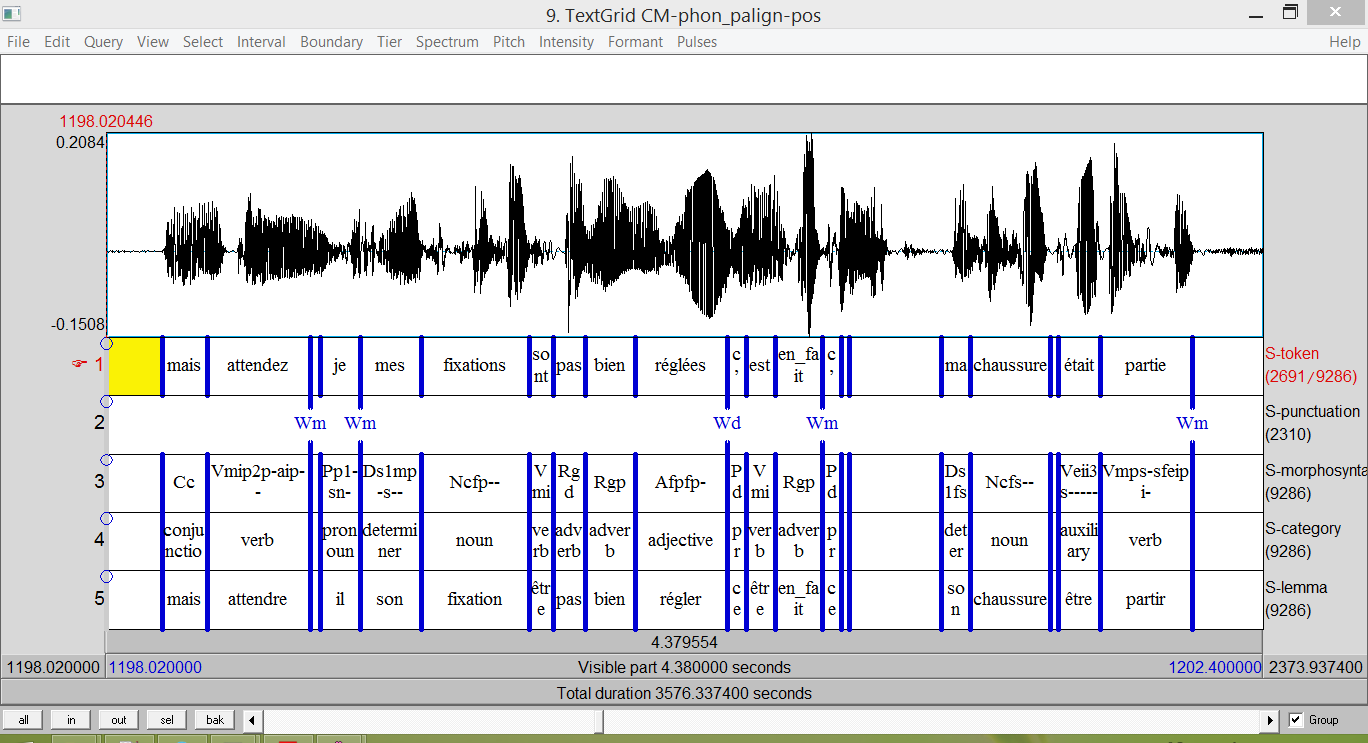
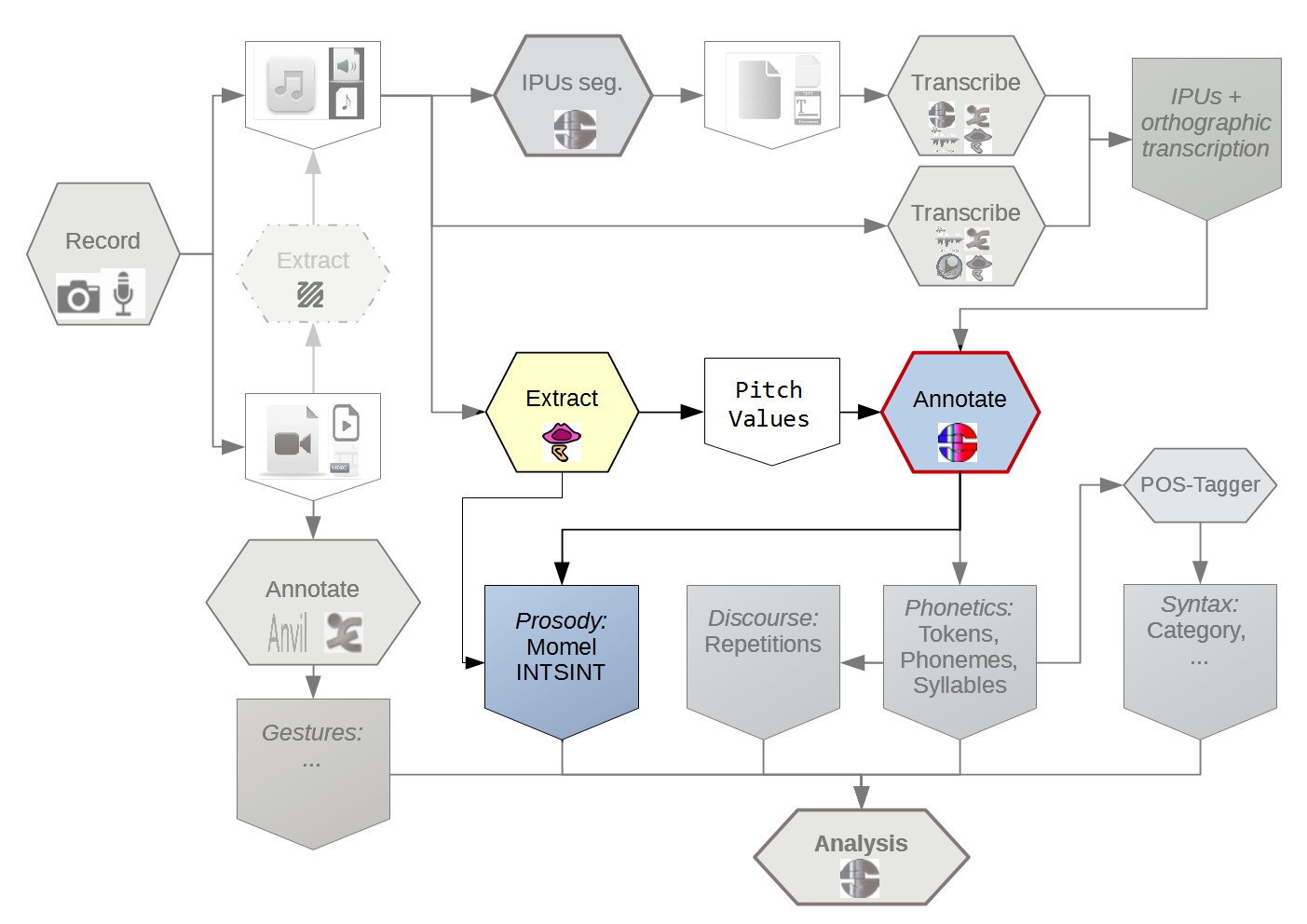
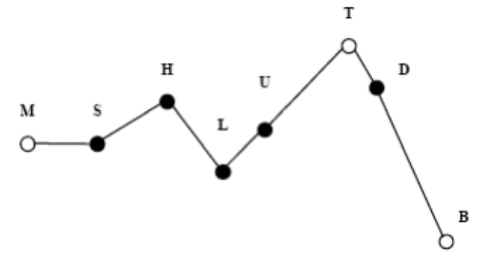
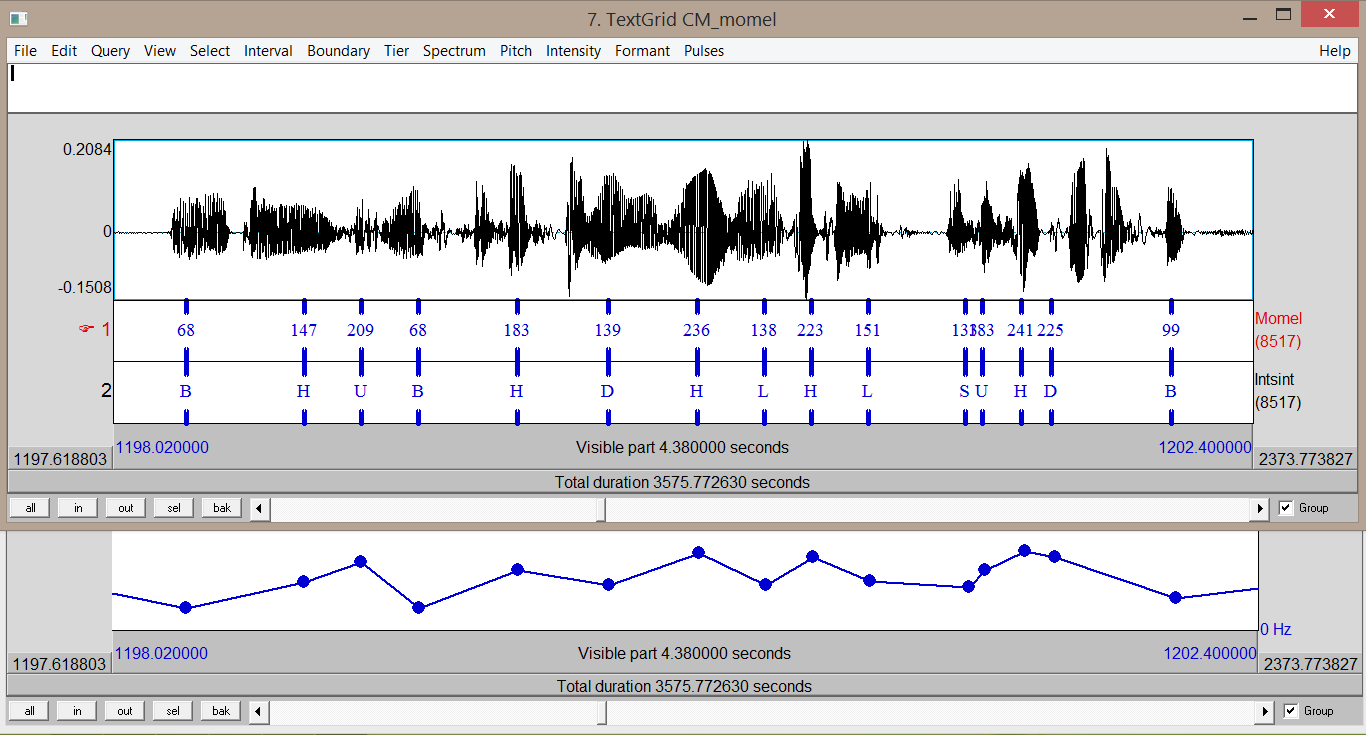
(Hirst and Espesser, 1993)
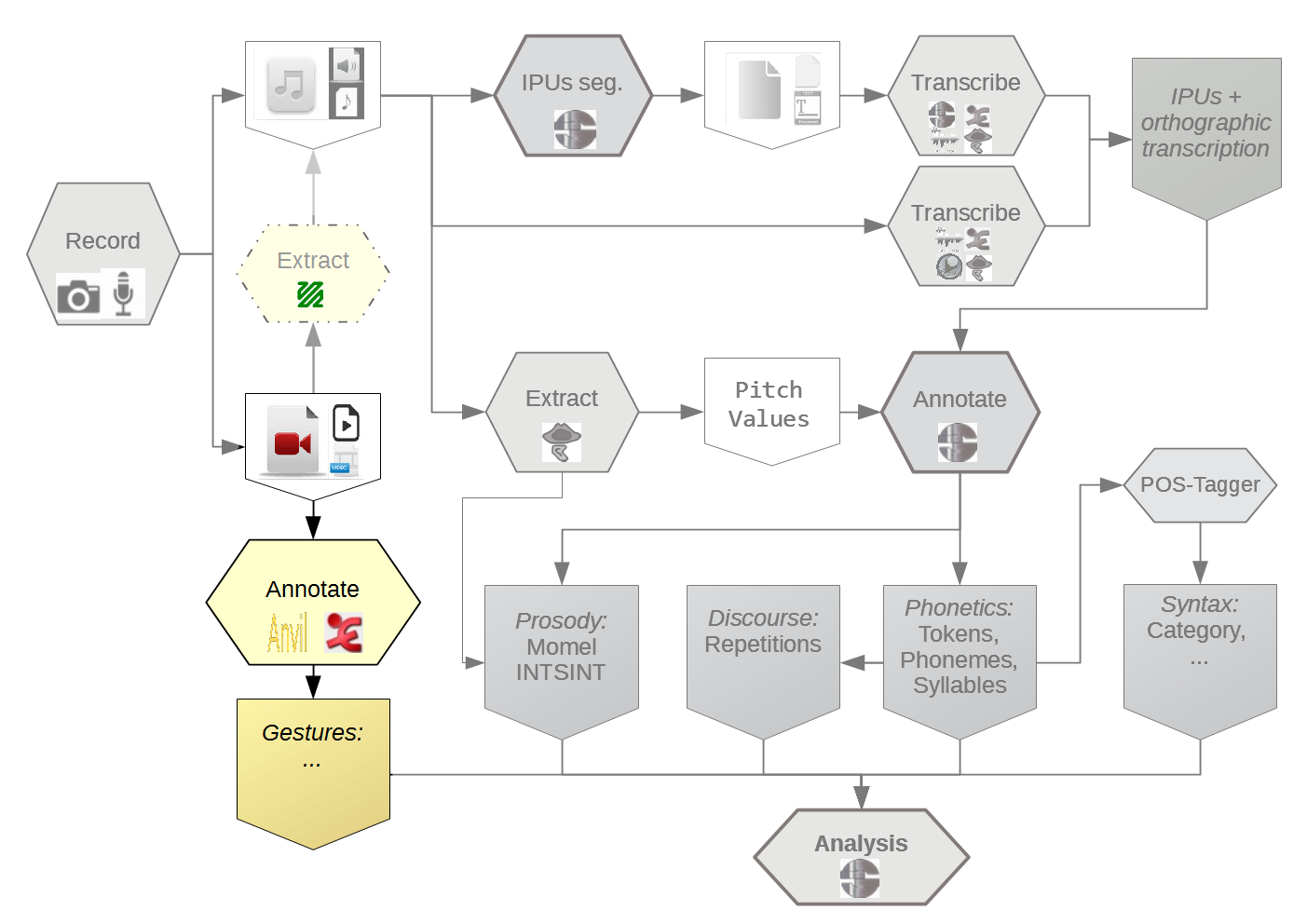
(Tellier 2014)