Examples of SPPAS Solutions
Table of content
Before using SPPAS
A SPPAS Solution for Speech Segmentation
- Step 1: Search for IPUs
- Step 2: Orthographic transcription
- Step 3: Text normalization
- Step 4: Phonetization
- Step 5: Alignment
A SPPAS Solution for Selfies Segmentation
Prepare the data
Description:
Examples of this tutorial are performed on the "Demo" files. In this way, you can follow the instructions and test yourself on these files.
The audio and video files are provided in the SPPAS packages, or, you can download directly from the following links:
Ready to start?
Launch the GUI of SPPAS then add both files in the workspace and check at least one of them, or open a Terminal application and change directory to the one of the SPPAS package.
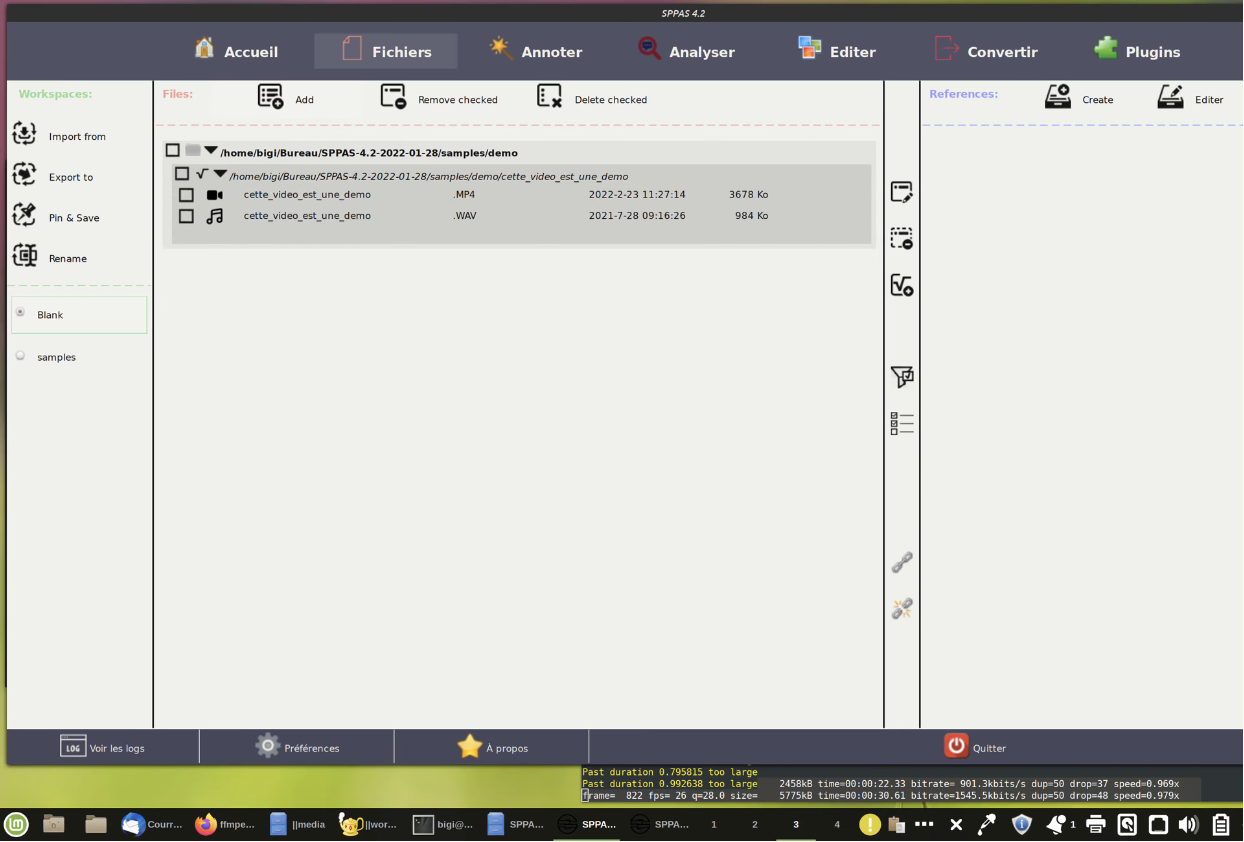
A SPPAS Solution for Speech Segmentation
Speech segmentation is the alignment of the speech recording with a phonetic transcription of the speech. SPPAS offers various solutions to perform it fully automatically or semi-automatically. This example is one of these solutions.
This solution starts with a semi-automatic macro-segmentation: the automatic search for Inter-Pausal Units (e.g. sounding segments) then the manual orthographic transcription. Three automatic annotations are then performing speech segmentation: Text Normalization, Phonetization and Alignment.
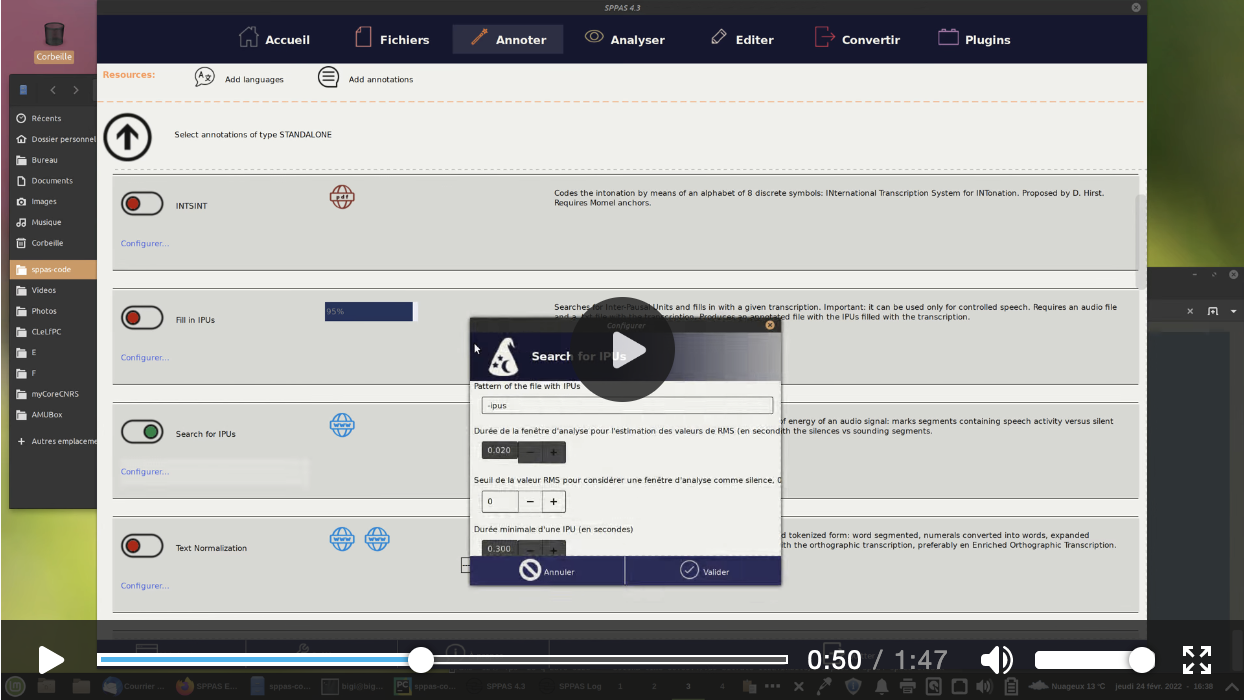
Step 1: Search for IPUs
What is it?
Given a speech recording, the goal of this task is to generate an annotation file in which the sounding segments between silences are marked. There are several parameters that must be fixed to get the expected result. Read the following paper:
Brigitte Bigi, Béatrice Priego-Valverde (2019). Search for Inter-Pausal Units: application to Cheese! corpus. In 9th Language & Technology Conference: Human Language Technologies as a Challenge for Computer Science and Linguistics, pp. 289-293, Poznań, Poland.
What are the input/output files?
Search for IPUs requires an audio file: the better quality, the better result! Supported format is WAV with only one channel.

How can you do?
Use the GUI or the CLI to perform the STANDALONE "Search for IPUs" automatic annotation. In the given example, there's no need to change the default parameters because it's read speech in French language.
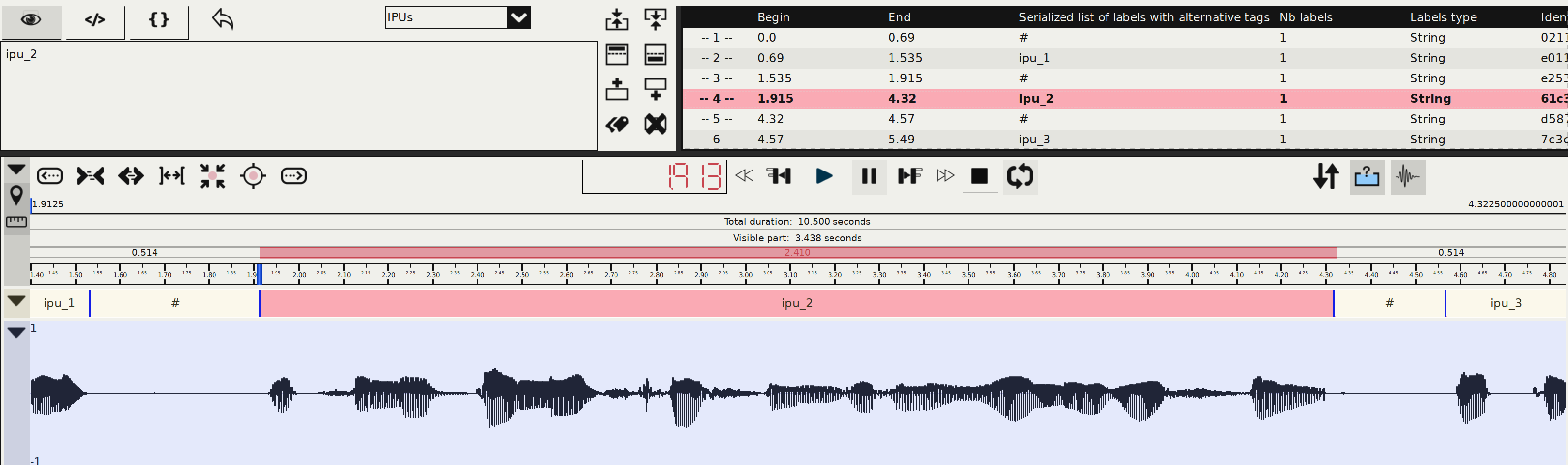
What's the result?
The result is an annotated file indicating boundaries of the sounding segments. It contains only one tier with name "IPUs". However, if the resulting sounding segments are not like you expected, it means either:
- the audio file is of poor quality;
- parameters were not properly configured.
Step 2: Orthographic transcription
What is it?
An orthographic transcription is often the minimum requirement for a speech corpus; it is at the top of the annotation procedure, and it is the entry point for most of the automatic annotations. A transcription convention is designed to provide rules for writing speech corpora. This convention establishes what are the phenomena to transcribe and also how to mention them in the orthography. From the beginning of its development, it was considered to be essential for SPPAS to deal with an Enriched Orthographic Transcription (EOT).
The SPPAS package contains the PDF of the transcription convention, or it can be downloaded from here.
Brigitte Bigi, Pauline Péri, Roxane Bertrand (2012). Orthographic Transcription: which enrichment is required for phonetization? In Proceedings of the Eight International Conference on Language Resources and Evaluation, pp. 1756–1763, Istanbul, Turkey.
What are the input/output files?
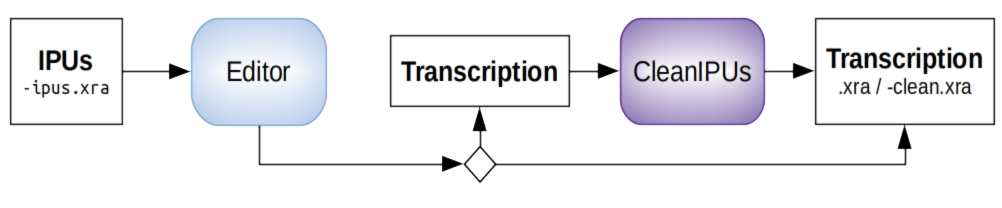
How can you do?
Whatever the solution you choose, the result of this step must be an annotation file (xra, textgrid, eaf, mrk...) with the orthographic transcription time-aligned at the IPUs level.
The following is a 100% SPPAS solution:
- In the page "Files" of the GUI, check the file with IPUs;
- Open it in the 'Analyze' page of the GUI;
- Click "New file" and set the same name, at the same location, but without the "-ipus" pattern;
- Copy/Paste the tier with the IPUs in this newly created file;
- Rename the "IPUs" tier into "Transcription";
- Optionally, edit metadata to add annotator information;
- Save and close all.
- Check both the audio and the new file;
- Open them both in the page "Edit";
- Listen and transcribe each IPU, move boundaries when required;
- Click to save, then "Close all".
Notice that the page "Edit" of the GUI is still under development. Any constructive comment or suggestion or bug report is welcome.
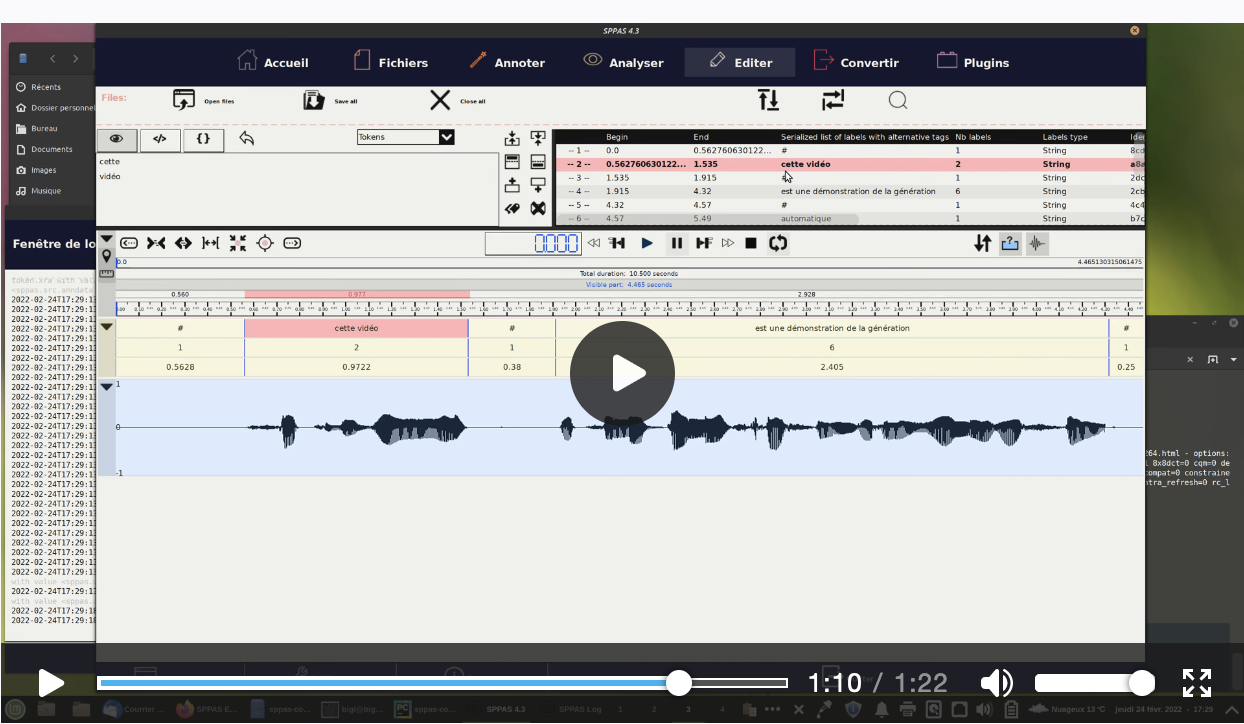
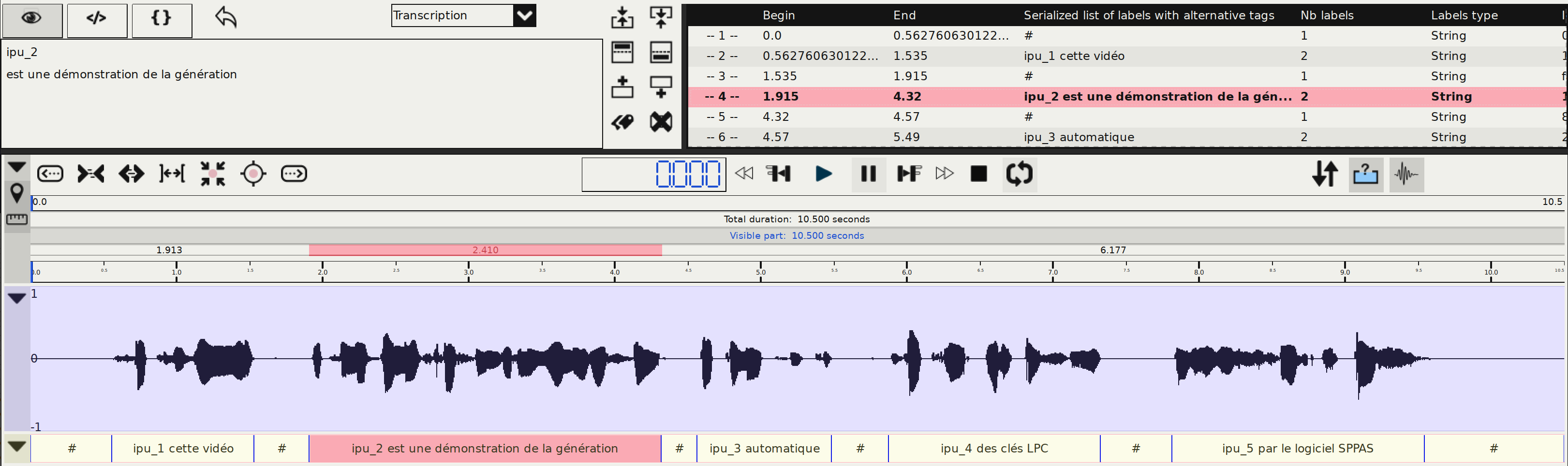
What is the result?
The result is an annotated file with an exact orthographic transcription performed into the IPUs.
Step 3: Text normalization
What is it about?
The first task faced by any speech or language processing system is the conversion of input text/transcription into a linguistic representation. Speech transcriptions contain truncated words, orthographic reductions, etc. Normalizing or rewriting such texts using ordinary words is an important issue for various applications. Among the essential steps of building a corpus, word segmentation is a necessary but highly challenging task for some languages. SPPAS implements a generic approach, i.e., a text normalization method as language and task independent as possible.
Brigitte Bigi (2014). A Multilingual Text Normalization Approach. Human Language Technology Challenges for Computer Science and Linguistics, LNAI 8387, pp. 515–526.
What are the input/output files?
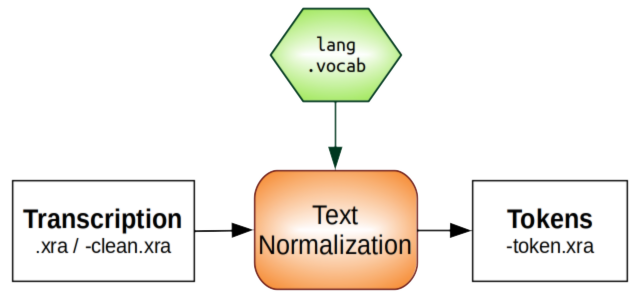
How to do it?
Use the GUI or the CLI to perform the Text Normalization STANDALONE
automatic annotation. Select "fra" language. In the GUI, you can check
the option Create a tier with the standard tokens
, but for this
file, it is not really useful because it's read speech, so we didn't
transcribe any specific mispronounciation or other phenomena.

What is the result?
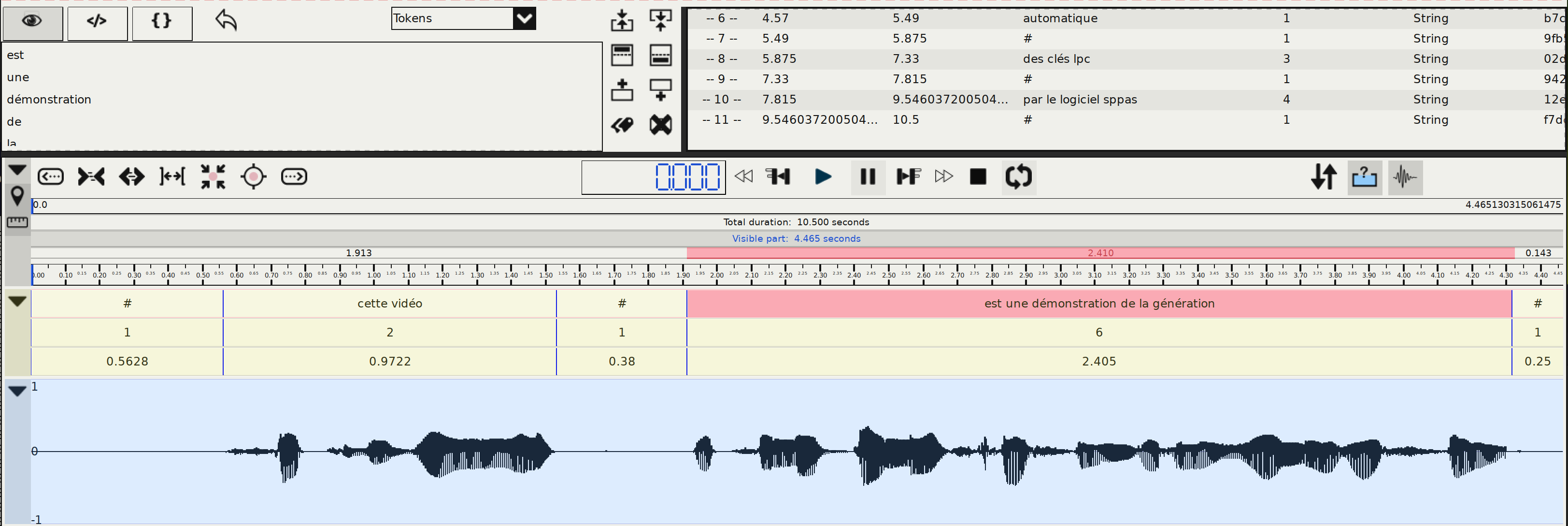
Step 4: Phonetization
What is it about?
Phonetization is the process of representing sounds by phonetic symbols. The program for the phonetization of the orthographic transcription produces a phonetic transcription based on a phonetic dictionary. An important step is then to build the pronunciation dictionary, where each word in the vocabulary is expanded into its constituent phones. You can customize the pronounciation dictionaries of SPPAS: do it yourself!
Brigitte Bigi (2016). A phonetization approach for the forced-alignment task in SPPAS. Human Language Technology. Challenges for Computer Science and Linguistics, LNAI 9561, pp. 515–526.
What are the input/output files?
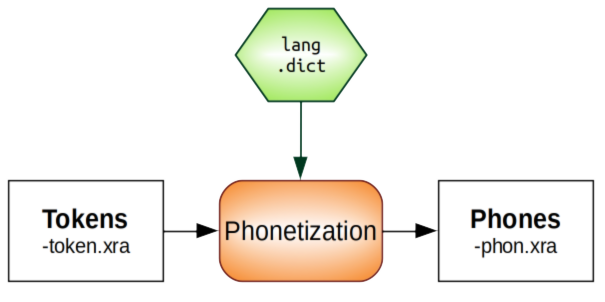
How to do it?
Use the GUI or the CLI to perform the Phonetization STANDALONE automatic annotation. Select "fra" language.

What is the result?
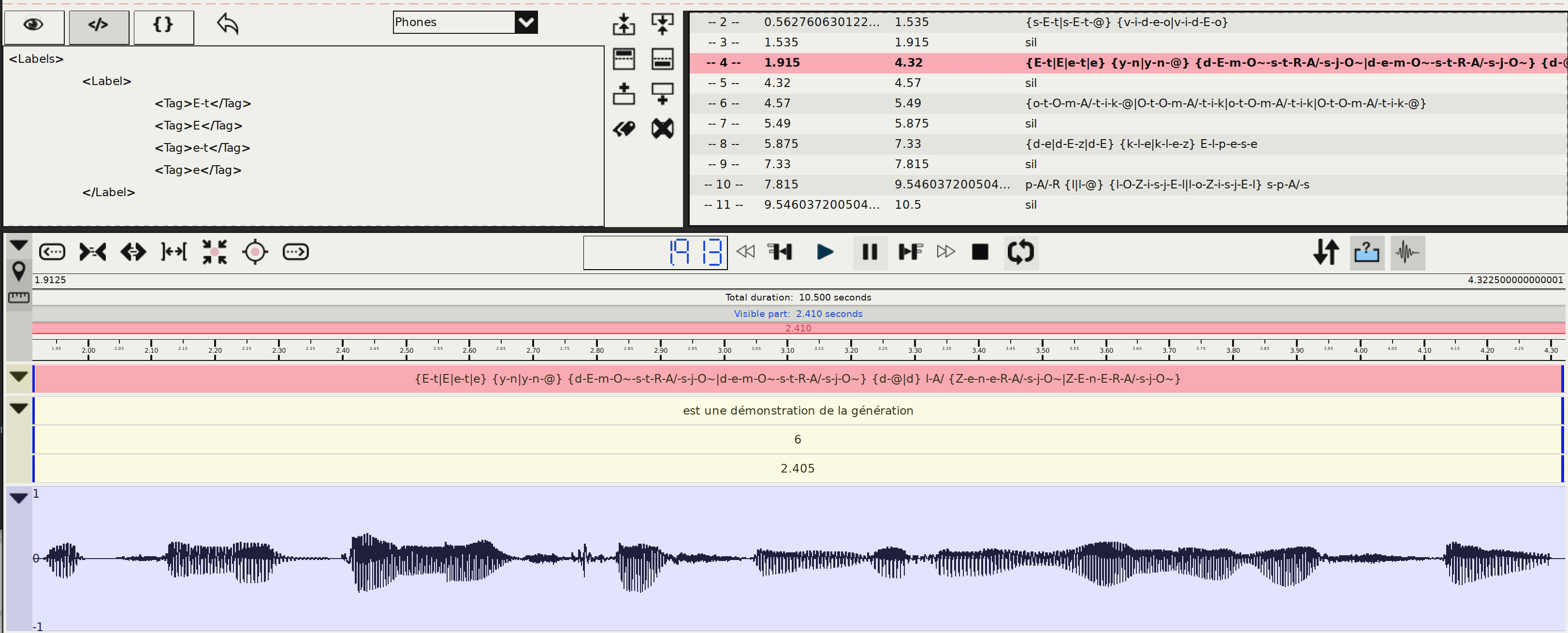
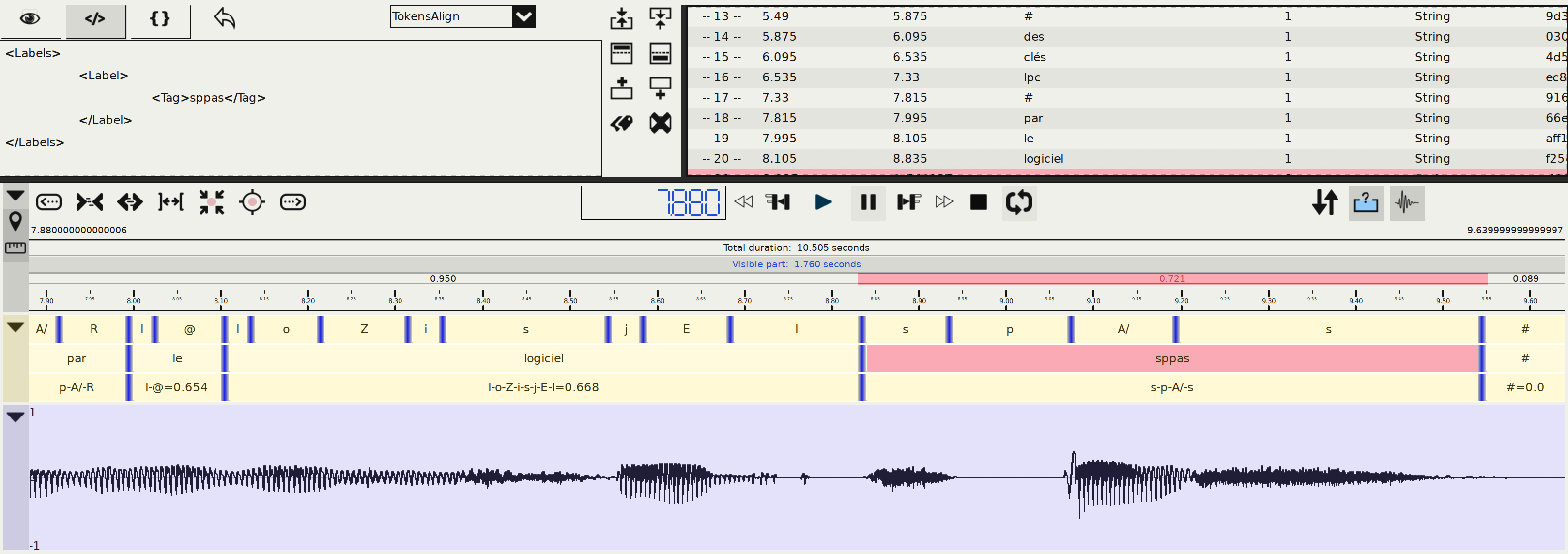
Step 5: Alignment
What is it about?
Phonetic alignment consists in a time-matching between a given speech utterance and a phonetic representation of the utterance. SPPAS is based on the Julius Speech Recognition Engine. For each utterance, the orthographic and phonetic transcriptions are used. Julius performs an alignment to identify the temporal boundaries of phones and words.
Brigitte Bigi, Christine Meunier (2018). Automatic segmentation of spontaneous speech. Revista de Estudos da Linguagem. International Thematic Issue: Speech Segmentation, 26(4), pp. 1489-1530
What are the input/output files?
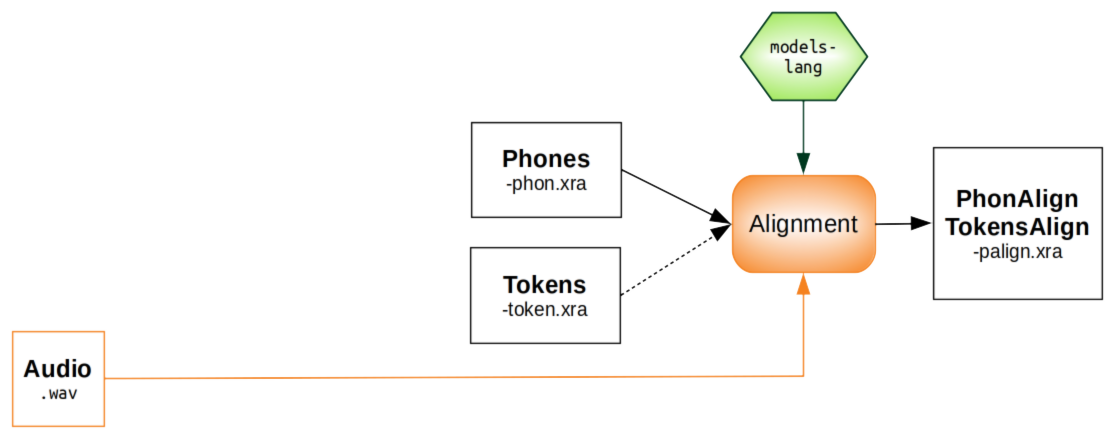
How to do it?
Use the GUI or the CLI to perform the Alignment STANDALONE automatic annotation. Select "fra" language. This annotation requires the program "Julius CSR Engine" (or HVite from HTK-Toolkit).

What is the result?
A SPPAS Solution for Selfies Segmentation
All the following annotations require the "video" feature to be enabled.
Face detection is requiring models that are not installed by default. In the GUI, click the "Add annotations" button and follow instructions.
Step 1: Face detection
How to do it?
Notice that this annotation can be very (very very) slow, and the higher video framerate and image size, the slower it is!

One of the possible results
Step 2: Person Face identity
By default, the annotation will produce one file with all detected persons and one file for each detected person.